Olá Pessoal,
Fiz este resumo sobre pontos mais importantes do IPv6 para ser didático, compreensível e objetivo. O nível de abrangência deste resumo ficaria num ponto intermediário entre as certificações CCNA e BSCI. Segue abaixo.
IPv6
– Foi adicionado diversas funcionalidades se comparado com o IPv4, tais como: 128 bits para endereçamento (IPv4 apenas 32), segurança (através de extension headers), técnicas para transição de IPv4 para IPv6, QOS embebbed (direto no header), autoconfiguration (permite um host obter um endereço IP sem ter que rodar um DHCP na rede) e mobilidade IP.
– O endereço IPv6 possui 128 bits e é dividido em 8 ‘sextetos’, cada um com 16 bits.
– O Header (incluindo IPs de origem e destino) possui 320 bits, sem as extensões – apresentado abaixo.
– IPv6 não possui o campo checksum (e nem o realiza) por considerar que o controle de erros das camadas inferiores é confiável.
– IPv6 não usa broadcast, e sim multicast. Um broadcast poderia ser simulado enviando um multicast para o endereço All-nodes, escopo Link-local (FF02::1).
– Endereço de Loopback – ::1/128 (IPv4 = 127.0.0.1). Endereço default-route – ::0/0 (IPv4 = 0.0.0.0/0).
– EUI-64: formato derivado do MAC-address utilizado para se atribuir endereços Link-Local. É pego o MAC address (48 bits), inserido o número hexadecimal FFFE no meio dele e modificado os primeiros 2 bits (de 00 para 20), portanto o MAC 00eb.1234.3322 no formato EUI-64 ficaria: 02eb:12ff:fe34:3322. Enfim, agregando o prefixo para endereços Link-local teríamos: FE80::02eb:12ff:fe34:3322.
– Tipos de endereços IPv6:
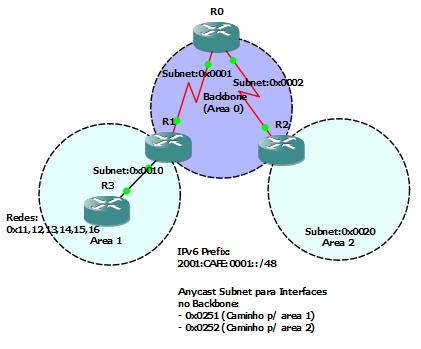
- Global Unicast: Identifica um host único na Internet. Serão atribuidos prefixos para cada organização (48 bits ou menos), como visto na figura. A IANA definiu o prefixo para estes prefixos como 2000::/3.

- Link-Local: Cada interface recebe um destes endereços. É utilizado para os dispositivos na mesma rede se comunicarem sem ter de utilizar o endereço Global Unicast. Utilizam o Prefixo FE80::/10 + o formato EUI-64.
- Site-local. Endereço único dentro do escopo da organização, não roteável na Internet. Prefixo: FEC0::/10.
– Multicast: Identificado pelo prefixo FF00::/8. Os próximos 4 bits são flags, e os outros 4 próximos definem o escopo do Multicast (apresentados abaixo). Ao lado, é apresentado um esquema da abrangência dos escopos.
- 1 = Interface-local.
- 2 = Link-local.
- 5 = Site-local.
- 8 = Organization-local.
- E = Global.
– Anycast: Um endereço Global Unicast atribuido a mais de um dispositivo, definido-o como anycast. Tem como função rotear para o dispositivo anycast mais próximo. Veja abaixo.
– Hosts Ipv6 devem responder pelo menos nos seguintes endereços:
- Global Unicast e Anycast (2000::/3)
- Link-local (FE80::/10, por autoconfiguration
- Loopback (::1/128)
- All-nodes Multicast (FF01::1 e FF02::1)
- Outro grupo multicast atribuido.
– Roteadores, além de responder neste endereços devem ainda responder em:
- Endereço Anycast da subrede (endereço da subrede com o Interface ID – endereço do host – setado em 0)
- All-routers Multicast (FF01::2, FF02::2, FF05::2)
- Grupos de multicast definidos por protocolos de roteamento (se aplicável). EIGRP for IPv6: FF02::10, OSPFv3: FF02::5 (todos Routers) e FF02::6 (apenas DR e BDR).
– As principais formas de transição do IPv4 para IPv6 pode ser feita através do Dual Stack (rodar ambos IPv4 e IPv6 até não ter mais necessidade de IPv4) e Tunelamento (encapsular o pacote IPv6 dentro de um pacote IPv4 – figura). Para o tunelamento é previsto o prefixo 2002::/16.

Referências
– CCNP BSCI Official Exam Certification Guide 4th edition, por Brent Stewart. CiscoPress
– CCNA 4.1 Guia Completo de Estudo, por Marco Filippetti. Visual Books
– CertProject, imagem do header IPv6.
– Cisco IOS IPv6 Multicast Introduction – MT BOM.
– RFC 3513 Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing.
Gostaria de dedicar apoio especial a todos que estarão se certificando ao longo do mês de junho.
Um grande abraço,
Maurício Bento Ghem.Hello Guys,
I did this summary on the most important of IPv6 to be didactic, comprehensive and objective. The level of coverage of this summary would be midway between BSCI and CCNA certifications. Below.
IPv6
– We added several features compared to IPv4, such as 128 bits for addressing (IPv4 only 32), security (through extension headers), techniques to transition from IPv4 to IPv6, QOS embebbed (direct the header), Autoconfiguration ( allows a host to obtain an IP address without having to run DHCP on the network) and IP mobility.
– The IPv6 address has 128 bits and is divided into 8 ‘sextet’, each with 16 bits.
– The Header (including the source and destination IP) has 320 bits, without the extensions – below.

– IPv6 does not have the checksum field (and not the place), considering that the control of errors of lower layers is reliable.
– IPv6 USA not broadcast, but multicasting. A broadcast can be simulated by sending a multicast address to the All-nodes, link-local scope (FF02:: 1).
– Loopback Address -:: 1 / 128 (IPv4 = 127.0.0.1). Address default-route -: 0 / 0 (IPv4 = 0.0.0.0 / 0).
– EUI-64: format derived from the MAC-address used to assign addresses Link-Local. You get the MAC address (48 bits), the hexadecimal number FFFE inserted in the middle of it and changed the first 2 bits (from 00 to 20), so the MAC 00eb.1234.3322 in EUI-64 format would be: 02eb: 12ff: fe34: 3322. Finally, adding the prefix for link-local addresses would: FE80:: 02eb: 12ff: fe34: 3322.
– Types of IPv6 addresses:
- Global Unicast: Identifies a single host on the Internet. Prefixes will be assigned to each organization (48 bits or less), as seen in the picture. The IANA defines the prefix for these prefixes like 2000:: / 3.

- Link-Local: Each interface receives one of these addresses. It is used for the devices on the same network to communicate without having to use the Global Unicast address. Use the prefix FE80:: / 10 + the EUI-64 format.
- Site-local. Single address within the scope of the organization, not routable on the Internet. Prefix: FEC0:: / 10.
– Multicast: Identified by prefix FF00:: / 8. The next 4 bits are flags, and the other 4 next define the scope of Multicast (shown below). Beside, a diagram of the range of scopes.

- 1 = Interface-local.
- 2 = link-local.
- 5 = site-local.
- 8 = Organization-local.
- E = Global.
– Anycast: A Global Unicast address assigned to more than one device, set it as anycast. Has as its route to the nearest anycast device. See below.

– IPv6 Hosts must meet at least the following addresses:
- Global Unicast and Anycast (2000:: / 3)
- Link-local (FE80:: / 10, by Autoconfiguration
- Loopback (:: 1 / 128)
- Multicast all-nodes (FF01:: 1 and FF02:: 1)
- Another group multicast assigned.
– Routers, and this answer should also respond in address:
- Anycast address of the subnet (the subnet address with the Interface ID – Host address – set to 0)
- All-Multicast routers (FF01:: 2, FF02:: 2, FF05:: 2)
- Groups defined by multicast routing protocols (if applicable). EIGRP for IPv6: FF02:: 10, OSPFv3: FF02:: 5 (all routers) and FF02:: 6 (only DR and BDR).
– The main forms of transition from IPv4 to IPv6 can be made through the Dual Stack (running both IPv4 and IPv6 to no longer have need for IPv4) and tunneling (encapsulate the IPv6 packet within an IPv4 packet – figure). For the tunneling is expected the prefix 2002:: / 16.
References:
– CCNP BSCI Official Exam Certification Guide 4th edition, por Brent Stewart. CiscoPress
– CCNA 4.1 Guia Completo de Estudo, por Marco Filippetti. Visual Books
– CertProject, imagem do header IPv6.
– Cisco IOS IPv6 Multicast Introduction – Very good.
– RFC 3513 Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing.
I would pay special support to all who will make sure during the month of June.
A big hug,
Maurício Bento Ghem.